In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, CTOs face an increasingly familiar paradox: the urgent need for skilled engineers coupled with the glacial pace of traditional hiring processes.
While business demands accelerate and digital transformation initiatives multiply, the conventional recruitment pipeline remains frustratingly slow, often taking months to deliver the talent needed yesterday.
The Critical Challenge
This challenge has reached a critical inflection point. Organisations across industries are recognising that waiting for the perfect permanent hire can mean:
- Missing market opportunities
- Delaying product launches
- Watching competitors surge ahead
The traditional hiring bottleneck has evolved from a minor inconvenience to a strategic liability that can determine market success or failure.
Enter IT Staff Augmentation
IT Staff Augmentation transforms how forward-thinking CTOs build and scale their engineering capacity. Unlike traditional outsourcing models, staff augmentation offers:
- Agility to rapidly deploy specialised talent
- Control over project outcomes and team dynamics
- Flexibility to scale based on actual needs
This comprehensive guide explores how savvy technology leaders are leveraging this approach to break free from hiring constraints and build truly agile engineering organisations.
The Hidden Costs of Traditional Hiring Bottlenecks
Time-to-Market Delays: The Silent Revenue Killer
Every day spent waiting for the right hire represents potential revenue walking out the door. Consider the ripple effects:
Immediate Impact:
- Product launches get postponed
- Feature releases are delayed
- Critical system improvements remain backlogged
Competitive Consequences:
- Competitors move swiftly to capture market share
- First-mover advantages slip away
- Customer acquisition opportunities are missed
Long-term Effects:
- Strategic setbacks compound over time
- Market momentum becomes difficult to recover
- Brand positioning weakens against agile competitors
Key Insight: The modern market rewards speed and agility. Companies that can rapidly respond to user feedback hold significant advantages over those constrained by resource limitations.
Internal Resource Strain: The Burnout Cascade
While waiting for new hires, existing team members inevitably shoulder additional responsibilities. This creates a dangerous cycle:
Phase 1: Initial Strain
- Temporary coverage becomes sustained overwork
- Code quality decreases under pressure
- Technical debt accumulates rapidly
Phase 2: Quality Degradation
- Overworked engineers produce lower-quality code
- Debug time increases significantly
- Project timelines extend further
Phase 3: Talent Flight Risk
- Valuable existing talent seeks more sustainable environments
- Knowledge drain compounds resource problems
- Bridging Skill Gaps becomes nearly impossible
The Mentoring Bottleneck: Senior engineers find themselves juggling multiple roles simultaneously:
- Coding critical features
- Mentoring junior developers
- Managing project timelines
- Handling customer escalations
Opportunity Cost Analysis: The Innovation Penalty
The most damaging aspect of hiring bottlenecks? The opportunities that never materialise.
Immediate Losses:
- Innovation projects get shelved indefinitely
- Experimental initiatives are postponed
- Strategic technology investments are delayed
Strategic Consequences:
- Organisations enter “maintenance mode” thinking
- Technology stacks become increasingly outdated
- Future modernisation efforts become exponentially more complex
Competitive Impact:
- Agile competitors capture emerging opportunities
- Market positioning weakens over time
- Revenue potential remains unrealised
Understanding IT Staff Augmentation: Beyond Traditional Outsourcing
What Makes Staff Augmentation Different?
IT Staff Augmentation represents a fundamental shift from traditional outsourcing models:
| Traditional Outsourcing | IT Staff Augmentation |
|---|---|
| Hand off entire projects | Integrate skilled professionals into existing teams |
| Limited internal oversight | Maintain direct management control |
| Formal communication channels | Daily collaboration and real-time feedback |
| Vendor manages resources | You manage augmented team members directly |
The Integration Advantage
Modern IT Staff Augmentation emphasises seamless integration:
Technical Integration:
- Same development tools and environments
- Identical coding standards and review processes
- Shared project management systems
- Unified testing and deployment pipelines
Cultural Integration:
- Participation in daily standups and planning sessions
- Contribution to architectural decisions
- Alignment with organisational values
- Investment in team success and project outcomes
Three Core Augmentation Models
1. Project-Based Staff Augmentation
- Best For: Discrete initiatives with defined timelines
- Key Benefits: Intensive focus on specific deliverables, specialised expertise, clear engagement boundaries, and measurable ROI.
- Ideal Scenarios: System migrations, new product development, technology stack modernisations, compliance implementations.
2. Long-Term Capacity Building
- Best For: Consistent supplemental resources
- Key Benefits: Stable additional capacity, ongoing support, team scalability with relationship continuity, and reduced onboarding overhead.
- Ideal Scenarios: Sustained growth periods, specialized technology maintenance, geographic expansion support, seasonal demand fluctuations.
3. Flexible Resource Augmentation
- Best For: Variable workload management
- Key Benefits: Rapid scaling, cost optimization, access to diverse skill sets, and maximum organizational agility.
- Ideal Scenarios: Agile development cycles, multi-phase projects, experimental technology adoption, economic uncertainty.
Strategic Framework for Implementing Staff Augmentation
Phase 1: Comprehensive Assessment
Current State Analysis
- Quantitative Evaluation: Team size vs. workload, project velocity, resource utilization, cost per feature.
- Qualitative Assessment: Skill gap identification, process bottleneck analysis, team satisfaction, cultural readiness.
Future State Planning
- Capacity Forecasting: Planned launches, seasonal patterns, strategic initiatives, market demands.
- Skills Roadmap: Emerging tech adoption, legacy system modernization, compliance needs, innovation projects.
Phase 2: Partner Selection Criteria
Technical Expertise Verification
- Live coding exercises, architecture discussions, code reviews, and technical communication assessment.
Integration Readiness
- Familiarity with your tech stack, agile methodologies, DevOps practices, and remote collaboration tools.
Cultural Fit Assessment
- Communication excellence, collaborative problem-solving, and team integration potential.
Security and Compliance Standards
- Due diligence on background checks, security clearances, compliance certifications, and data handling protocols.
Phase 3: Integration Excellence
Accelerated Onboarding
- Technical Setup: Environment configuration, access provisioning, tool familiarization, codebase orientation.
- Team Introduction: Role clarification, communication protocols, meeting cadence, cultural norm explanation.
Knowledge Management
- Documentation standards, code review processes, architecture decision recording, and capturing lessons learned.
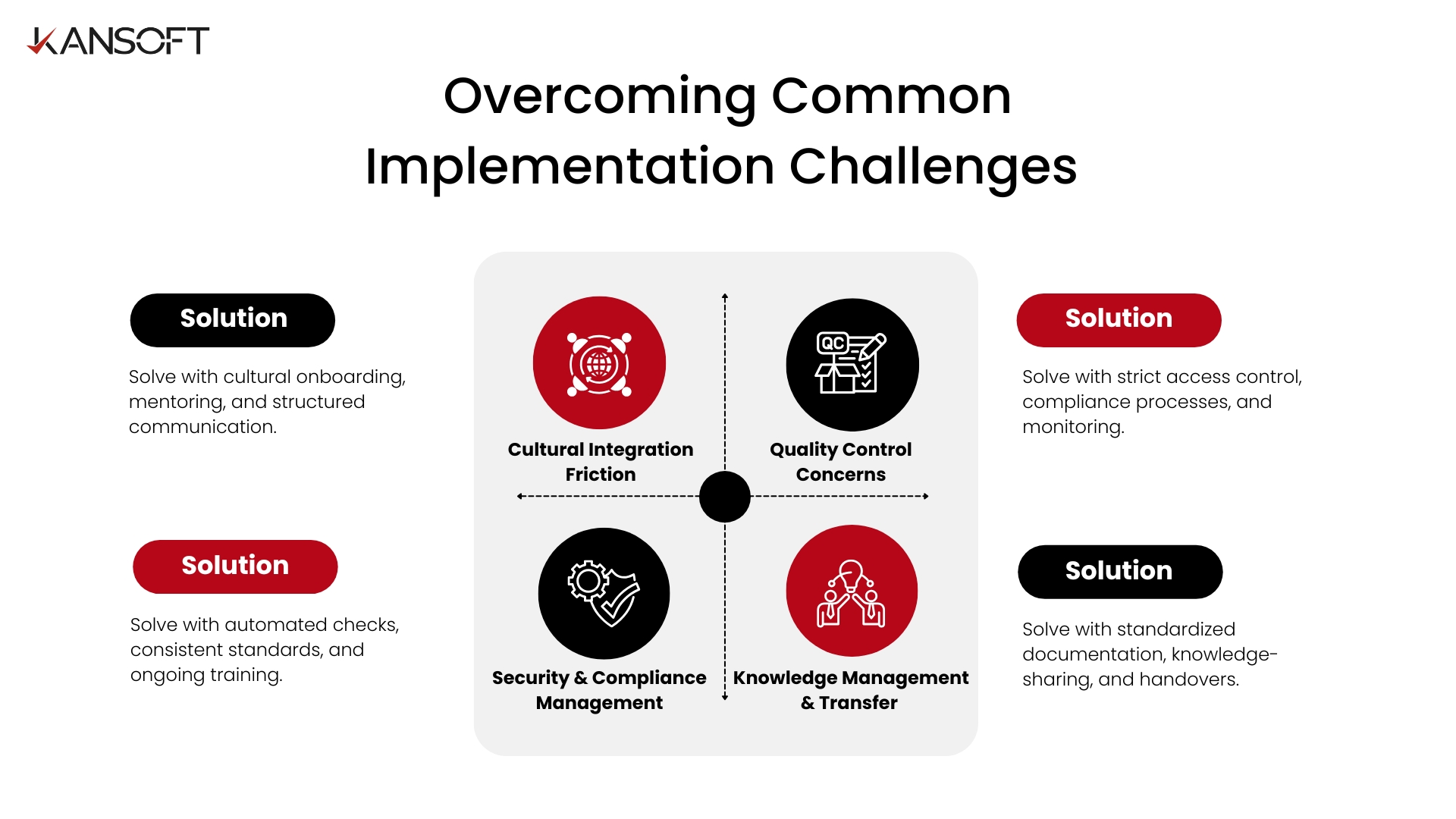
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Challenge 1: Cultural Integration Friction
- Problem: Mismatch in collaborative culture, rigid structures, or conflicting communication styles.
- Solution: Implement comprehensive cultural onboarding with mentors, enhance communication protocols with regular feedback, and establish clear escalation paths.
Challenge 2: Quality Control Concerns
- Problem: Variation in quality standards, inconsistent processes, and lack of organizational context.
- Solution: Establish a systematic quality framework with automated gates, comprehensive review checklists, and clear documentation on standards and architecture.
Challenge 3: Security and Compliance Management
- Problem: Complex access control, data protection requirements, and maintaining audit trails.
- Solution: Use a robust security framework with just-in-time access, regular reviews, activity monitoring, and thorough compliance integration for training and verification.
Challenge 4: Knowledge Management and Transfer
- Problem: Institutional knowledge gaps and the risk of losing expertise when engagements end.
- Solution: Implement structured knowledge transfer with mandatory documentation, regular sharing sessions, mentoring, and comprehensive handover protocols.
Conclusion
IT Staff Augmentation has evolved from a tactical response to hiring challenges into a strategic imperative. CTOs who embrace this approach gain significant advantages in agility, expertise, and scalability.
The Competitive Advantage
Strategic Benefits:
- Flexible resourcing to respond to market opportunities
- Enhanced innovation through access to diverse expertise
- Risk mitigation with reduced long-term commitments
- Accelerated learning and internal capability building
The Path Forward
Success depends critically on choosing the right augmentation partner. Organizations that partner with experienced providers like Kansoft gain access to not just skilled resources, but strategic expertise and proven methodologies.
The question isn’t whether to embrace staff augmentation, but how quickly you can implement it with the right partner. As digital transformation accelerates, the ability to rapidly access specialized talent will determine market success. IT Staff Augmentation with a proven partner like Kansoft provides the strategic flexibility needed to thrive.